Emotional trading is one of the most common pitfalls that many investors and traders face, yet it often leads to significant financial losses. In the world of trading and investing, emotions like fear, greed, and anxiety can cloud judgment and lead to irrational decision-making. This article will explore what emotional trading is, the psychological factors behind it, its effects on investment outcomes, and effective strategies to mitigate its negative impact.
What is Emotional Trading?
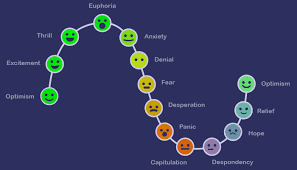
Emotional trading refers to making investment or trading decisions based on emotional impulses rather than rational analysis or sound strategy. Common emotions like fear and greed often dominate an investor’s thinking, especially when markets are volatile. Instead of sticking to a predetermined trading plan or following a strategy, emotional traders react to short-term market fluctuations, news, or personal biases, which can lead to impulsive and poor decision-making.
For example, an investor may buy into a stock out of greed when its price surges, driven by the fear of missing out (FOMO). Similarly, a trader might sell off an asset in panic during a market downturn, only to regret the decision once the market recovers.
The Psychology Behind Emotional Trading
The human brain is hardwired to react emotionally to certain stimuli, which plays a significant role in emotional trading. Several psychological factors contribute to emotional trading, including:
1. Loss Aversion
Loss aversion is a cognitive bias where the pain of losing is psychologically more impactful than the pleasure of gaining. This leads emotional traders to take excessive risks to avoid realizing losses or to exit positions prematurely to avoid further decline. For instance, an investor might hold onto a losing position for too long, hoping the market will turn around, despite evidence suggesting that the asset is unlikely to recover soon.
2. Fear of Missing Out (FOMO)
The fear of missing out, or FOMO, occurs when traders buy into a rising market or a hot asset without conducting thorough research or analysis. They worry that if they don’t act quickly, they will miss the opportunity for high returns. This emotional response can lead to chasing price movements, which often results in buying at the peak and suffering losses when the market corrects.
3. Overconfidence Bias
Overconfidence bias leads traders to believe that they have more knowledge or control over the market than they actually do. This bias can result in riskier decisions, as the trader may ignore sound risk management techniques or take overly aggressive positions. Overconfident traders may also disregard market signals that contradict their assumptions, leading to losses.
4. Anchoring Bias
Anchoring bias occurs when traders base their decisions on irrelevant information, such as the price at which they originally purchased an asset. For example, if a trader buys a stock at $50 and the price drops to $40, they may irrationally hold onto the stock, thinking it will return to the original price, even if the fundamentals of the company have changed.
5. Herd Mentality
Traders often fall prey to the herd mentality, where they make decisions based on what other traders or the general public is doing. This is especially evident during market bubbles or crashes, when investors collectively buy or sell without fully understanding the reasons behind the trend. The herd mentality can lead to speculative bubbles and exacerbate market volatility.
How Emotional Trading Impacts Investment Performance
Emotional trading can have disastrous effects on an investor’s portfolio. Some of the key negative impacts include:
1. Increased Risk-Taking
When emotions such as greed or fear take control, traders are more likely to take on excessive risks. They may over-leverage their positions or engage in speculative trading, which can result in large losses. Overconfidence and FOMO can cause traders to ignore proper risk management strategies, ultimately damaging their long-term financial goals.
2. Impulsive Decisions
Emotional trading often leads to impulsive decisions, such as buying or selling assets without conducting proper analysis. This lack of planning and strategy can lead to poor investment choices and suboptimal returns. For instance, buying during a market rally based on fear of missing out or selling during a market downturn out of panic can lock in losses at the wrong time.
3. Chasing Losses
Emotional traders often engage in a behavior known as “chasing losses.” When they experience a loss, they may attempt to recover their money quickly by making riskier trades, hoping for a quick rebound. This cycle of attempting to recoup losses often leads to even greater financial setbacks.
4. Decreased Consistency
Successful investing relies on consistency and discipline, but emotional trading undermines both. Emotional decisions often lead to erratic trading patterns, which make it difficult to adhere to a long-term investment strategy. The lack of consistency can prevent traders from capitalizing on the long-term potential of their investments.
Strategies to Overcome Emotional Trading
While emotional trading can be detrimental, it is possible to manage and mitigate its impact by implementing certain strategies. Here are some effective techniques for overcoming emotional trading:
1. Develop a Trading Plan
One of the best ways to avoid emotional trading is to develop a clear and comprehensive trading plan. A trading plan should include your investment goals, risk tolerance, asset allocation, and entry and exit strategies. By adhering to your plan, you can avoid making impulsive decisions based on market fluctuations or emotional reactions. A well-defined plan can help you stay focused on your long-term objectives and reduce the temptation to act on emotions.
2. Use Stop-Loss Orders
Stop-loss orders are an effective risk management tool that can help mitigate emotional decision-making. A stop-loss order automatically triggers the sale of an asset if its price falls below a specified level. This strategy helps limit potential losses and prevents emotional traders from holding onto losing positions out of fear or hope that prices will recover.
3. Practice Mindfulness and Emotional Awareness
Being mindful of your emotional state while trading is crucial. Recognize when fear, greed, or other emotions are influencing your decisions. Practicing emotional awareness can help you avoid making rash decisions in the heat of the moment. Techniques like deep breathing, meditation, or taking a break from the screen can help calm your emotions and bring clarity to your decisions.
4. Set Realistic Expectations
Setting realistic expectations and understanding that losses are a natural part of trading can help manage emotional reactions. By accepting that not every trade will be profitable, you can reduce the emotional impact of losses. Similarly, avoiding the temptation to chase unrealistic gains can help curb the effects of greed and FOMO.
5. Diversify Your Portfolio
Diversifying your investment portfolio is another way to reduce emotional trading. A well-diversified portfolio can help mitigate the impact of short-term market fluctuations and provide a buffer against emotional decision-making. When your investments are spread across different asset classes, you are less likely to be influenced by the movements of a single asset.
6. Use Trading Journals
Maintaining a trading journal can be a useful tool for tracking your emotions and decision-making processes. By reviewing your trades, you can identify patterns of emotional trading and learn from past mistakes. A journal can also help you stay accountable to your trading strategy and keep emotions in check.
Conclusion
Emotional trading can significantly impair your investment strategy and lead to poor financial outcomes. By understanding the psychological factors that drive emotional trading, such as fear, greed, and overconfidence, investors can take proactive steps to manage their emotions and avoid impulsive decisions. Developing a solid trading plan, setting realistic expectations, using risk management tools, and practicing emotional awareness are all essential strategies for overcoming emotional trading. By adopting these practices, investors can enhance their decision-making process, improve their chances of success, and achieve long-term financial goals.