Introduction
The Forex market analysis is the foundation of successful currency trading. With a daily trading volume exceeding $7 trillion, the foreign exchange (Forex) market is the largest and most liquid financial market in the world. Whether you’re a beginner or a seasoned trader, mastering the art of market analysis is essential to make informed decisions, manage risk, and capitalize on global economic trends.
This guide explores the three main types of Forex market analysis—technical, fundamental, and sentiment—and how traders can combine them to gain a competitive edge.
1. What Is Forex Market Analysis?
Forex market analysis involves evaluating the currency market to predict price movements and make trading decisions. Unlike stock or commodity markets, Forex is influenced by a unique set of factors, including interest rates, geopolitical stability, central bank policy, and economic data releases.
There are three primary approaches to Forex analysis:
- Technical Analysis
- Fundamental Analysis
- Sentiment Analysis
Each method provides different insights, and the most successful traders often blend these strategies for a well-rounded view.
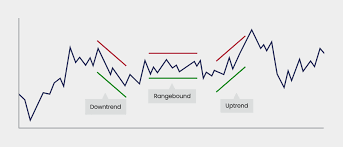
2. Technical Analysis: Chart Patterns & Indicators
Technical analysis focuses on historical price data and trading volumes. Traders use charts, patterns, and indicators to identify trends, support/resistance levels, and potential reversals.
Key Tools in Technical Forex Analysis:
- Candlestick Patterns: Help identify bullish/bearish trends (e.g., doji, engulfing, hammer).
- Moving Averages: Smooth price data to spot trends (e.g., SMA, EMA).
- Relative Strength Index (RSI): Measures overbought or oversold conditions.
- MACD (Moving Average Convergence Divergence): Indicates momentum and trend reversals.
- Fibonacci Retracement: Predicts potential pullback levels.
Technical traders believe that “price reflects everything,” so they rarely consider news or economic reports.
3. Fundamental Analysis: Economic Forces Driving Currency Values
Fundamental analysis examines the macroeconomic indicators and news events that influence a currency’s value. This includes interest rates, inflation, employment, GDP growth, and geopolitical events.
Core Elements of Fundamental Forex Market Analysis:
- Central Bank Policies: Interest rate decisions by the Federal Reserve, ECB, BoJ, etc., impact currency strength.
- Economic Indicators: NFP (Non-Farm Payrolls), CPI, PMI, retail sales, and GDP reports shape market expectations.
- Political Events: Elections, trade wars, or geopolitical tensions can cause volatility.
- Commodity Prices: For currencies like the Canadian dollar (CAD) or Australian dollar (AUD), oil and metal prices are critical.
A strong economy generally strengthens its currency, while instability tends to weaken it.
4. Sentiment Analysis: Reading the Crowd
Sentiment analysis gauges how traders and investors feel about a particular currency pair. While hard to quantify, it plays a vital role in short-term price movements.
Sentiment Analysis Tools:
- Commitment of Traders (COT) Reports: Shows institutional positions.
- Retail Positioning: Brokers like IG provide data on the percentage of long vs. short positions.
- News Headlines & Social Media Trends: Can influence trader sentiment dramatically.
When sentiment is overly bullish or bearish, it may signal a reversal is imminent—a concept known as “contrarian trading.”
5. Combining All Three Approaches
No single type of analysis is perfect. The best Forex traders blend technical, fundamental, and sentiment analysis to validate trades.
For example:
- Use fundamental analysis to determine the overall trend (e.g., a hawkish Fed suggests a strong USD).
- Use technical analysis to time entries and exits.
- Use sentiment analysis to gauge if the market is overcrowded or contrarian opportunities exist.
This multi-dimensional approach allows traders to act with greater confidence and adapt to shifting market conditions.
6. Tools and Platforms for Forex Analysis
Today’s traders have access to a wide array of tools that simplify Forex market analysis:
- MetaTrader 4/5 (MT4/MT5): Industry-standard platforms with built-in indicators and expert advisors.
- TradingView: Web-based charting with community-shared ideas and scripts.
- Economic Calendars: Track major economic events (e.g., Investing.com, ForexFactory).
- News Feeds: Bloomberg, Reuters, and central bank websites for real-time data.
- AI Tools & Bots: Increasingly used for sentiment and data-driven trading strategies.
7. Common Mistakes in Forex Market Analysis
Many traders fall into predictable traps:
- Over-reliance on indicators: Using too many can create “analysis paralysis.”
- Ignoring fundamental events: News can override technical setups.
- Misreading sentiment: Crowded trades can snap back quickly.
- Lack of risk management: No amount of analysis can substitute for a solid stop-loss strategy.
The key is to balance analysis with discipline and adaptability.
Conclusion
Forex market analysis is an essential pillar of currency trading. By understanding and applying technical, fundamental, and sentiment-based insights, traders can navigate volatility, identify profitable setups, and avoid costly mistakes.
As the global economy becomes increasingly interconnected and fast-moving, the ability to analyze the Forex market with depth and nuance offers a clear competitive advantage.
Whether you’re trading EUR/USD, GBP/JPY, or emerging markets, consistent and informed Forex market analysis is your best tool for long-term success.