Risk-taking behavior is a natural part of human life. From investing in the stock market to starting a new business or even choosing a risky path in personal relationships, risk-taking is inherent in many of our daily decisions. However, while some risk-taking can lead to great rewards, it also carries significant consequences. Understanding the dynamics of risk-taking behavior—including why we take risks, the different types of risks, and how to manage them—can provide valuable insights into making better decisions, both personally and professionally.
What is Risk-Taking Behavior?
Risk-taking behavior refers to the tendency to engage in actions or decisions that involve a potential for significant loss or gain. It can occur in various contexts, such as financial investments, career choices, physical activities, or even social interactions. In general, risk-taking involves stepping into the unknown with an understanding that there is uncertainty about the outcome.
Risk-taking can be classified into two categories:
- Calculated Risks: These are risks that are taken after careful consideration, analysis, and weighing of the potential outcomes.
- Reckless Risks: These are risks taken impulsively, without adequate consideration of potential consequences.
Understanding the balance between these two types of risk is key to making informed decisions.
The Psychology Behind Risk-Taking Behavior
Risk-taking behavior is influenced by a combination of psychological, emotional, and social factors. Some of the key psychological drivers behind risk-taking include:
- Personality Traits
Certain personality traits are associated with higher levels of risk-taking. For instance, individuals who are high in traits such as openness to experience, sensation-seeking, or extraversion are more likely to engage in risky behaviors. These people may seek out new and exciting experiences and find pleasure in taking risks. - Emotions and Impulsivity
Strong emotions like excitement, fear, or anger can cloud judgment and influence risk-taking behavior. People may take risks to alleviate feelings of boredom, stress, or frustration, or simply to experience the adrenaline rush associated with risky activities. - Social Influence
Peer pressure and societal norms play a significant role in risk-taking behavior. In group settings, individuals may engage in risky behaviors they wouldn’t normally consider if they were alone, especially when they see others taking similar risks. - Past Experiences
Past experiences and previous exposure to risk can influence one’s propensity to take risks in the future. For example, someone who has experienced success after taking a risk in the past may be more inclined to take similar risks again, believing in the potential for reward.
Types of Risk-Taking Behaviors
Risk-taking behavior can manifest in a variety of ways. Some common types include:
- Financial Risk-Taking
One of the most common areas of risk-taking involves financial decisions, such as investing in the stock market, buying real estate, or starting a business. These types of decisions carry the risk of financial loss but also the potential for substantial gain. - Physical Risk-Taking
Physical risk-taking behaviors include activities such as extreme sports, dangerous driving, or unsafe physical stunts. These behaviors can lead to serious injury or even death but are often motivated by a desire for adventure or personal achievement. - Social Risk-Taking
Social risks include behaviors like speaking in public, entering new social situations, or making personal decisions that may affect social relationships. Social risk-taking is often linked to self-esteem and personal development. - Health Risk-Taking
Engaging in unhealthy habits like smoking, excessive drinking, or drug use are forms of risk-taking behavior that can have long-term negative consequences on one’s health.
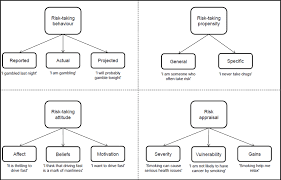
The Impact of Risk-Taking Behavior
Risk-taking behavior can have both positive and negative outcomes, depending on how it is managed and the context in which it occurs. Here’s a breakdown of both sides:
Positive Impacts:
- Innovation and Progress
Many groundbreaking innovations, whether in technology, business, or science, arise from individuals or groups who are willing to take calculated risks. Entrepreneurs, for example, often need to take risks to create new products, enter new markets, and push boundaries. - Personal Growth and Achievement
Risk-taking can lead to personal growth and the achievement of goals. Stepping outside of your comfort zone—whether by public speaking, trying a new career path, or traveling to unfamiliar places—can boost confidence, broaden perspectives, and lead to a sense of accomplishment. - Financial Gains
In the realm of investment, risk-taking can lead to significant financial rewards. Investors who take calculated risks may reap substantial returns from stocks, real estate, or other financial ventures.
Negative Impacts:
- Financial Loss
Reckless financial risk-taking, such as gambling or speculative investments, can lead to severe financial losses and even bankruptcy. These types of risks often lack careful analysis and can leave individuals in precarious financial positions. - Physical Injury
Engaging in dangerous activities without proper precautions can result in injuries or even death. Risky behaviors such as reckless driving, extreme sports, or unsafe work practices can have life-altering consequences. - Strained Relationships
Social risk-taking, especially when it involves impulsive decisions or behavior that others perceive as irresponsible, can lead to conflicts, broken relationships, or loss of social standing.
How to Manage Risk-Taking Behavior
While risk-taking can be beneficial in certain contexts, it’s important to strike a balance and manage risks effectively. Here are a few strategies to manage risk-taking behavior:
- Evaluate Risks and Rewards
Before taking any significant risks, carefully evaluate the potential rewards against the possible losses. This involves considering factors such as the probability of success, potential financial or personal consequences, and the likelihood of achieving the desired outcome. - Develop Self-Control and Impulse Management
Being able to resist impulsive decisions is key to reducing reckless risk-taking. Practicing mindfulness, setting clear goals, and delaying gratification can help individuals make more measured decisions. - Learn from Experience
Reflect on past risk-taking experiences to understand what worked and what didn’t. Learning from mistakes can help individuals refine their decision-making and avoid repeating costly errors. - Consult Experts
When considering high-stakes risks, whether financial or physical, seeking advice from experts can provide valuable insights and help mitigate potential downsides.
Conclusion
Risk-taking behavior is an essential part of life, driving innovation, personal growth, and achievement. However, it also comes with its own set of challenges and consequences. By understanding the psychological factors behind risk-taking, recognizing different types of risks, and managing the behavior responsibly, individuals can unlock the benefits of risk while minimizing potential harm. Whether you’re making investment decisions, trying a new adventure, or navigating social situations, learning how to assess and balance risk can lead to greater success in all areas of life.