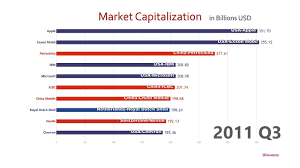
Price fluctuations are an integral part of economic markets. Whether you’re dealing with commodities, currencies, or stocks, price fluctuations are inevitable and can have significant effects on businesses, investors, and consumers alike. This article delves into the causes of price fluctuations, the impact they have on the economy, and strategies that businesses and individuals can use to mitigate the risks associated with them.
What Are Price Fluctuations?
Price fluctuations refer to the continuous rise and fall in the value of a commodity, stock, currency, or any other financial instrument. These changes can occur over short or long periods and are often influenced by a wide range of factors, including market demand, economic conditions, and geopolitical events. Understanding price fluctuations is crucial for anyone participating in markets, as these changes can significantly impact profitability, investment strategies, and economic stability.
Causes of Price Fluctuations
- Supply and Demand Dynamics
The most fundamental cause of price fluctuations is the principle of supply and demand. When demand for a product or service exceeds supply, prices tend to rise. Conversely, when supply exceeds demand, prices generally fall. For example, during a shortage of crude oil, oil prices surge, while an oversupply results in price drops. This can be observed in various sectors, from agricultural products to technology stocks.
- Economic Factors
Economic factors such as inflation, interest rates, and GDP growth significantly influence price fluctuations. When a country experiences inflation, the purchasing power of its currency decreases, leading to higher prices for goods and services. Similarly, interest rate changes can impact the cost of borrowing, influencing both consumer spending and business investment, which in turn affects the prices of goods and services.
- Market Sentiment
Market sentiment, driven by consumer confidence and investor expectations, can also cause price fluctuations. Positive sentiment often leads to higher demand and rising prices, while negative sentiment can lead to decreased demand and falling prices. For instance, when consumers believe the economy is thriving, they are more likely to make big purchases, driving up prices. In contrast, during times of economic uncertainty, consumer and investor behavior may lead to price declines.
- Geopolitical Events and Natural Disasters
Geopolitical events, such as wars, trade disputes, and political instability, can lead to significant price fluctuations. These events often create uncertainty in the markets, causing investors to reassess risk, which can lead to volatility. Natural disasters, such as hurricanes or earthquakes, can also disrupt production and supply chains, leading to sudden price increases for certain goods, especially in sectors like agriculture, energy, and commodities.
- Speculation
Speculation is a common driver of price fluctuations, particularly in financial markets. Traders and investors often buy and sell assets based on their expectations of future price movements rather than the asset’s current value. This speculative activity can cause prices to fluctuate wildly, especially in markets with lower liquidity or higher volatility.
Impacts of Price Fluctuations
- Business Profitability
For businesses, price fluctuations can have both positive and negative effects on profitability. For example, if the price of raw materials increases, production costs may rise, squeezing profit margins. On the other hand, a company that can sell its products at higher prices due to increased demand or limited supply can benefit from price fluctuations. However, businesses that rely heavily on price stability may find it difficult to manage sudden price changes.
- Investment Risks
For investors, price fluctuations present both opportunities and risks. Volatile markets can lead to significant gains if investors can predict price movements accurately. However, unpredictable fluctuations can also lead to substantial losses, particularly for those who rely on short-term trading strategies. Long-term investors might not be as affected by short-term price fluctuations but may still need to manage the risk associated with market volatility.
- Consumer Behavior
Consumers are also impacted by price fluctuations, particularly when it comes to essential goods like food, energy, and housing. Rising prices can lead to reduced purchasing power, forcing consumers to alter their spending habits. For instance, when gas prices rise, consumers may reduce driving, which can affect demand for other goods and services.
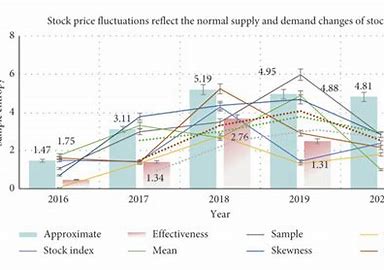
Strategies for Managing Price Fluctuations
- Hedging
One common strategy to manage price fluctuations, especially for businesses and investors, is hedging. Hedging involves taking an opposite position in a related asset or financial instrument to offset potential losses. For example, a company that relies on oil for production may hedge against rising oil prices by purchasing futures contracts. This helps lock in a price for the future, protecting the business from sudden price increases.
- Diversification
Diversification is another effective strategy to mitigate risk from price fluctuations. By spreading investments across various sectors or asset classes, businesses and investors can reduce their exposure to price swings in any single market. For example, an investor who holds a diversified portfolio of stocks, bonds, and commodities is less likely to be negatively affected by fluctuations in any one market.
- Long-Term Planning
For businesses, long-term planning is essential for managing price fluctuations. By anticipating potential price changes and incorporating these into their business strategies, companies can better absorb the impact of fluctuations. This might include securing long-term supply contracts, locking in prices with suppliers, or increasing inventory during periods of low prices to take advantage of future price hikes.
- Price Monitoring and Market Research
Businesses and consumers can also benefit from price monitoring and market research. By staying informed about market trends and economic indicators, companies can better anticipate price changes and make more informed decisions. Consumers, too, can track prices of essential goods to make smarter purchasing decisions.
Conclusion
Price fluctuations are an inevitable part of economic systems, but understanding their causes and impacts can help businesses, investors, and consumers navigate the volatility. By employing strategies like hedging, diversification, and long-term planning, individuals and organizations can manage the risks associated with price fluctuations. In a world of unpredictable markets, staying informed and prepared is key to minimizing the negative effects of price changes and capitalizing on potential opportunities.