Introduction
The stock market is a dynamic and essential part of the global economy. For both novice and experienced investors, understanding stock market analysis is crucial for making informed decisions. Stock market analysis involves the study of financial markets, individual stocks, and broader economic indicators to predict future market movements and identify profitable investment opportunities.
In this article, we will delve into the two main types of stock market analysis—fundamental analysis and technical analysis—explore the tools and techniques used by investors, and discuss strategies that can help optimize investment decisions.
What Is Stock Market Analysis?
Stock market analysis refers to the process of evaluating market trends, individual stocks, and economic factors to make informed investment decisions. The goal is to understand the forces that drive stock prices and forecast how those forces will influence future performance.
There are two primary approaches to stock market analysis:
- Fundamental Analysis
- Technical Analysis
Let’s explore each of these in more detail.
1. Fundamental Analysis
Fundamental analysis focuses on evaluating a company’s financial health, the industry in which it operates, and the broader economic environment to estimate its intrinsic value. This analysis involves examining the company’s balance sheet, income statement, and cash flow statement to assess key metrics such as:
- Earnings per Share (EPS): Indicates how much profit a company generates for each share of stock.
- Price-to-Earnings (P/E) Ratio: Helps investors determine if a stock is overvalued or undervalued relative to its earnings.
- Dividend Yield: Reflects the annual dividend income from a stock as a percentage of its current price.
- Return on Equity (ROE): Measures a company’s profitability relative to its shareholders’ equity.
- Debt-to-Equity Ratio: Indicates the level of debt a company has in comparison to its equity.
Fundamental analysts use this data to determine whether a stock is undervalued, overvalued, or fairly valued. By identifying stocks that are priced below their intrinsic value, investors can potentially profit from future price appreciation when the market corrects.
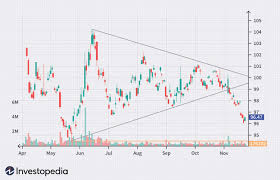
2. Technical Analysis
Technical analysis focuses on studying historical price movements and trading volumes to predict future price trends. Unlike fundamental analysis, technical analysis does not focus on a company’s financial health. Instead, it relies on charts, patterns, and indicators to assess market sentiment and investor behavior.
Some common tools used in technical analysis include:
- Moving Averages: A trend-following indicator that smooths out price data to identify trends over a specified period.
- Relative Strength Index (RSI): Measures the speed and change of price movements, helping investors identify overbought or oversold conditions.
- Bollinger Bands: A volatility indicator that shows how a stock’s price moves relative to its historical volatility.
- Candlestick Patterns: These patterns provide insights into market sentiment by visually representing the open, high, low, and close prices for a specific time period.
- Volume Analysis: Analyzes trading volume to confirm the strength of a price move.
Technical analysis is often used by short-term traders, such as day traders or swing traders, who rely on short-term price movements rather than long-term company fundamentals.
Key Factors Affecting Stock Market Trends
Several factors influence the stock market and play a vital role in stock market analysis:
1. Economic Indicators
Economic data such as GDP growth, unemployment rates, inflation, and interest rates have a significant impact on stock prices. Positive economic growth typically drives stock prices higher, while economic slowdowns or recessions can lead to a market decline.
2. Corporate Earnings
Corporate earnings reports are among the most critical events that influence stock prices. Investors closely watch earnings announcements to gauge whether companies are meeting or exceeding their revenue and profit expectations. Strong earnings can drive stock prices up, while disappointing earnings may lead to declines.
3. Market Sentiment and News
Investor sentiment and news events, such as political developments, natural disasters, or company-specific news, can influence market trends. Social media and online platforms can also quickly amplify market reactions, leading to sudden price swings.
4. Interest Rates and Monetary Policy
Central banks, such as the Federal Reserve in the U.S., control interest rates and monetary policy, which can impact stock market performance. Rising interest rates tend to make borrowing more expensive, reducing corporate profits and slowing down stock market growth. Conversely, lower interest rates often stimulate investment and economic activity, boosting stock prices.
5. Geopolitical Events
Geopolitical events, such as trade wars, conflicts, and international relations, can create uncertainty in the market, affecting investor confidence and stock prices.
Stock Market Analysis Strategies for Investors
Investors can use various strategies when analyzing the stock market to achieve optimal returns. Below are some popular strategies:
1. Long-Term Investment (Buy and Hold)
This strategy involves purchasing stocks based on fundamental analysis and holding them for an extended period. Long-term investors typically focus on companies with strong growth potential and stable financial health. The idea is to benefit from capital appreciation and dividends over time.
2. Value Investing
Value investing focuses on purchasing undervalued stocks with strong fundamentals. Investors look for stocks trading at a discount relative to their intrinsic value, betting that the market will eventually correct the pricing gap. Famous investors like Warren Buffett have popularized this strategy.
3. Growth Investing
Growth investors focus on companies with strong potential for future growth, even if they appear overpriced based on current financial metrics. This strategy often involves investing in industries like technology or biotechnology that are expected to see rapid expansion.
4. Swing Trading
Swing traders aim to profit from short-term price movements, holding stocks for several days or weeks. This strategy typically combines technical analysis with market sentiment to identify potential price swings.
5. Diversification
Diversification involves spreading investments across different sectors, asset classes, and geographical regions to reduce risk. By diversifying a portfolio, investors can minimize the impact of any single stock or market downturn on their overall performance.
Conclusion
Stock market analysis is a vital tool for investors seeking to make informed decisions and manage risk effectively. By understanding both fundamental and technical analysis, investors can better navigate market volatility and identify profitable opportunities.
As the stock market continues to evolve, it is important for investors to stay informed about key economic indicators, corporate earnings, and market sentiment. By employing diverse investment strategies such as value investing, growth investing, and diversification, investors can better position themselves for long-term success in the stock market.
Understanding stock market analysis empowers investors to make better decisions, whether they are pursuing short-term trades or long-term investments.